ArthritoMab™ Antibody Cocktail for Balb/c, DBA/1, R10.RIII, 50 mg
ArthritoMab™ Arthritis Inducing Antibody Cocktail is a cocktail of 4 arthritogenic monoclonal antibodies to collagen II (CII) used for inducing arthritis in the anti-Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) model. It is...
Antibodies
CIA-MAB-50
ArthritoMab™ Arthritis Inducing Antibody Cocktail is a cocktail of 4 arthritogenic monoclonal antibodies to collagen II (CII) used for inducing arthritis in the anti-Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) model. It is an excellent alternative to both the K/BxN and CIA models. Induction is rapid and results in a synchronized, steady and controlled disease progression that exhibits histological similarities to the classic CIA model. Download a protocol guide and data pack to learn more about the epitopes, protocol, optimization tips, positive controls and data.
The Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA) model is a relevant model for studying the efferent phase of RA, where leukocytes are attracted and respond to the immune complex in the joint. It is induced using a cocktail of antibodies to anti-CII and contains pathogenic features similar to that of RA such as pannus formation, cellular infiltration, synovitis and cartilage/bone destruction.
For use with C57BL/6, TG strains, see ArthritoMab™ Antibody Cocktail for C57BL/6, TG, 50 mg.
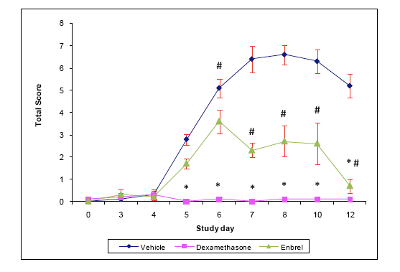
Figure: Balb/c were administered 2 mg of ArthritoMab antibody cocktail on day 0 followed by a LPS boost on day 3. Unlike competitor products, disease progression is steady and controlled for easy evaluation of prophylactic and therapeutic regimes.
Benefits of the CAIA model
- Length of study: Arthritis develops in mice typically within 24-48 hr allowing the completion of a study within 2 weeks reducing the number of assessments and scoring periods.
- Reduced group size: Rate of incidence is nearly 100% depending on the strain allowing for smaller group sizes.
- Synchronization: onset of disease is synchronized between animals simplifying treatment schedules.
- Steady & Controlled disease progression: No rapid & severe disease spikes enabling evaluation of all treatment schedules
- Susceptibility: Arthritis is induced not only in CIA-susceptible DBA/1 and B10.RIII mice, but also in some CIA-resistant mice, such as Balb/c.
- Eliminates expensive colonies: Models such as the K/BxN serum transfer model require labs to maintain expensive colonies and the sera can vary from batch to batch.
Comparison
|
|
ArthritoMab™ |
Competitor |
|
Epitopes Recognized |
CB11, CB10, CB8 |
CB11 only |
|
Disease Progression |
Steady & Controlled |
Rapid & Severe |
|
Paw involvement |
Consistent & Predominantely rear |
Variable & unpredictable |
|
Animals/vial |
25 |
20 |
Abreviations:
- Anti-Collagen Induced arthritis (ACIA)
- Monoclonal Antibody induced arthritis (mAb-RA)
- Collagen Antibody Induced Arthritis (CAIA)
References/Citations:
Marin, A. A., Decker, R. E., Kumar, S., Lamantia, Z., Yokota, H., Emrick, T., & Figueiredo, M. L. (2022). Enhancing Prednisone-Based Arthritis Therapy with Targeted IL-27 Gene Delivery. Bioengineering, 9(6), 248.
Van Mechelen, M., Hayer, S., Van Laere, K., Lories, R., & Neerinckx, B. (2022). AB0106 The Pattern of Joint Inflammation in the CAIA Mouse Model of Arthritis.
Sangaletti, S., Botti, L., Gulino, A., Lecis, D., Bassani, B., Portararo, P., ... & Colombo, M. P. (2020). SPARC regulation of PMN clearance protects from pristane induced lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Available at SSRN 3678911.
Nandakumar, K. S., Collin, M., Happonen, K. E., Lundström, S. L., Croxford, A. M., Xu, B., ... & Holmdahl, R. (2018). Streptococcal endo--N-acetylglucosaminidase suppresses antibody mediated inflammation in vivo. Frontiers in immunology, 9, 1623.
Hamamura, K., Nishimura, A., Chen, A., Takigawa, S., Sudo, A., & Yokota, H. (2015). Salubrinal acts as a Dusp2 inhibitor and suppresses inflammation in anti-collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Cellular signalling, 27(4), 828-835
Asnagli, H., Martire, D., Belmonte, N., Quentin, J., Bastian, H., Boucard-Jourdin, M., ... & Marchetti, I. (2014). Type 1 regulatory T cells specific for collagen type II as an efficient cell-based therapy in arthritis. Arthritis research & therapy, 16(3), R115
Ohtsubo-Yoshioka, M., Nunomura, S., Kataoka, T. R., Okayama, Y., & Ra, C. (2013). Fc receptor beta chain deficiency exacerbates murine arthritis in the anti-type II collagen antibody-induced experimental model. Modern rheumatology, 23(4), 804-810
Leavenworth, J. W., Tang, X., Kim, H. J., Wang, X., & Cantor, H. (2013). Amelioration of arthritis through mobilization of peptide-specific CD8+ regulatory T cells. The Journal of clinical investigation, 123(3), 1382-1389.
Jacques, P., Lambrecht, S., Verheugen, E., Pauwels, E., Kollias, G., Armaka, M., ... & Elewaut, D. (2013). Proof of concept: enthesitis and new bone formation in spondyloarthritis are driven by mechanical strain and stromal cells. Annals of the rheumatic diseases, annrheumdis-2013
Kudryavtseva, E., Forde, T. S., Pucker, A. D., & Adarichev, V. A. (2012). Wnt signaling genes of murine chromosome 15 are involved in sex‐affected pathways of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 64(4), 1057-1068
Te Boekhorst, B. C., Jensen, L. B., Colombo, S., Varkouhi, A. K., Schiffelers, R. M., Lammers, T., ... & Nicolay, K. (2012). MRI-assessed therapeutic effects of locally administered PLGA nanoparticles loaded with anti-inflammatory siRNA in a murine arthritis model. Journal of controlled release, 161(3), 772-780.
Dimitrova, P., Ivanovska, N., Belenska, L., Milanova, V., Schwaeble, W., & Stover, C. (2012). Abrogated RANKL expression in properdin-deficient mice is associated with better outcome from collagen-antibody-induced arthritis. Arthritis research & therapy, 14(4), R173.
Wruck, C. J., Fragoulis, A., Gurzynski, A., Brandenburg, L. O., Kan, Y. W., Chan, K., ... & Pufe, T. (2010). Role of oxidative stress in rheumatoid arthritis: insights from the Nrf2-knockout mice. Annals of the rheumatic diseases, annrheumdis132720
Min, S. H., Wang, Y., Gonsiorek, W., Anilkumar, G., Kozlowski, J., Lundell, D., ... & Grant, E. P. (2010). Pharmacological targeting reveals distinct roles for CXCR2/CXCR1 and CCR2 in a mouse model of arthritis. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 391(1), 1080-1086.
Hultqvist, M., Nandakumar, K. S., Björklund, U., & Holmdahl, R. (2009). The novel small molecule drug Rabeximod is effective in reducing disease severity of mouse models of autoimmune disorders. Annals of the rheumatic diseases, 68(1), 130-135.
Zalevsky, J., Secher, T., Ezhevsky, S. A., Janot, L., Steed, P. M., O’Brien, C., ... & Szymkowski, D. E. (2007). Dominant-negative inhibitors of soluble TNF attenuate experimental arthritis without suppressing innate immunity to infection. The Journal of Immunology, 179(3), 1872-1883.
Zalevsky, J., Secher, T., Janot, L., Wong, P., O'Brien, C., Ryffel, B., & Szymkowski, D. E. (2006, September). Preclinical efficacy of XPro (TM) 1595, a biologic dominant-negative inhibitor of soluble TNF that blocks inflammation without suppressing innate immunity. In ARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATISM (Vol. 54, No. 9, pp. S45-S45). DIV JOHN WILEY & SONS INC, 111 RIVER ST, HOBOKEN, NJ 07030 USA: WILEY-LISS.
Nandakumar, K. S., & Holmdahl, R. (2005). Efficient promotion of collagen antibody induced arthritis (CAIA) using four monoclonal antibodies specific for the major epitopes recognized in both collagen induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of immunological methods, 304(1-2), 126-136.
Product Insert (PDF) - Informational use only. Please refer to insert included with product.
Data/Specifications:
Epitope Specificity
The classic CIA model is mediated by autoantibodies which bind to type II collagen and complement. In mice as well as human RA patients, the antibody response that best correlates with disease is directed against the C1, J1 and U1 epitopes. The ArthritoMab™ arthritogenic cocktail of 4 monoclonal antibodies binds to these well-defined epitopes C11b, J1, D3 and U1, which are spread over the entire CII (CB8, CB10 and CB11 fragments). This possibly encourages better immune complex formation on the cartilage surface for the initiation of arthritis and produces consistent and predictable disease in all 4 paws (with predominance for the rear). Competitor products only recognize CB11, which produces variable disease that can contribute to unpredictable involvement in the paws (sometimes more front paw involvement and other times more rear involvement).
Susceptibility
- Balb/c
- DBA/1
- B10.RIII
- C57Bl/6
Disease Progression & Positive Controls
Disease progression is steady and controlled using ArthritoMab™ antibody cocktail, enabling investigators to evaluate various regimes. Data below was generated using Vehicle, Dexamethasone and Enbrel in the Balb/c strain (induced with 2 mg ArthritoMab™ on day 0 followed by LPS boost on day 3).