Featured Publication in Focus: ATP-binding cassette family C member 1 constrains metabolic responses to high-fat diet in male mice
Jul 25 , 2024
Authors:
Elisa Villalobos, Allende Miguelez-Crespo, Ruth A Morgan, Lisa Ivatt, Mhairi Paul, Joanna P Simpson, Natalie Z M Homer, Dominic Kurian, Judit Aguilar, Rachel A Kline, Thomas M Wishart, Nicholas M Morton, Roland H Stimson, Ruth Andrew, Brian R Walker and Mark Nixon
University/British Heart Foundation Centre for Cardiovascular Science, The Queen’s Medical Research Institute, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Society for Endocrinology. Journal of Endocrinology
----------------------
Product referenced:
Catalogue # M046006
----------------------
ABSTRACT
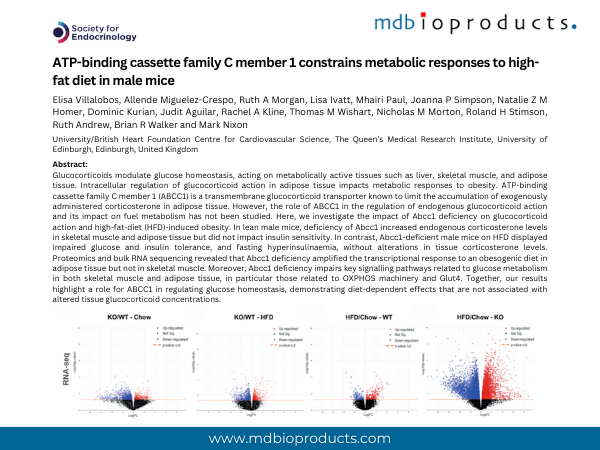
Glucocorticoids modulate glucose homeostasis, acting on metabolically active tissues such as liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue. Intracellular regulation of glucocorticoid action in adipose tissue impacts metabolic responses to obesity. ATP-binding cassette family C member 1 (ABCC1) is a transmembrane glucocorticoid transporter known to limit the accumulation of exogenously administered corticosterone in adipose tissue. However, the role of ABCC1 in the regulation of endogenous glucocorticoid action and its impact on fuel metabolism has not been studied. Here, we investigate the impact of Abcc1 deficiency on glucocorticoid action and high-fat-diet (HFD)-induced obesity. In lean male mice, deficiency of Abcc1 increased endogenous corticosterone levels in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue but did not impact insulin sensitivity. In contrast, Abcc1-deficient male mice on HFD displayed impaired glucose and insulin tolerance, and fasting hyperinsulinaemia, without alterations in tissue corticosterone levels. Proteomics and bulk RNA sequencing revealed that Abcc1 deficiency amplified the transcriptional response to an obesogenic diet in adipose tissue but not in skeletal muscle. Moreover, Abcc1 deficiency impairs key signalling pathways related to glucose metabolism in both skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, in particular those related to OXPHOS machinery and Glut4. Together, our results highlight a role for ABCC1 in regulating glucose homeostasis, demonstrating diet-dependent effects that are not associated with altered tissue glucocorticoid concentrations.
To continue reading and to download the publication:
