Featured Publication in Focus: Impaired Development of Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis in Rab44-Deficient Mice
Nov 13 , 2024
Authors:
Yu Yamaguchi, Tomoko Kadowaki, Eiko Sakai, Mayuko Noguromi, Shun Oyakawa and Takayuki Tsukuba
Department of Dental Pharmacology, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Nagasaki University, Nagasaki 852-8588, Japan
mdpi. biomedicines
----------------------
Products referenced:
Catalogue # CIA-MAB-2C
ArthritoMab™ Antibody Cocktail for C57BL/6, TG, 50 mg
Catalogue
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), 5.0 mg
----------------------
ABSTRACT
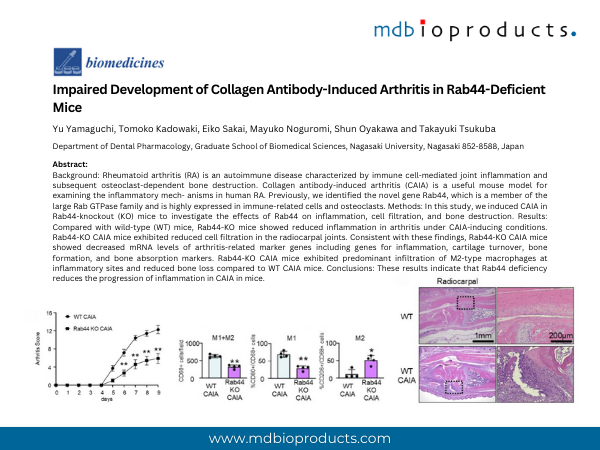
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease characterized by immune cell-mediated joint inflammation and subsequent osteoclast-dependent bone destruction. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis (CAIA) is a useful mouse model for examining the inflammatory mech- anisms in human RA. Previously, we identified the novel gene Rab44, which is a member of the large Rab GTPase family and is highly expressed in immune-related cells and osteoclasts. Methods: In this study, we induced CAIA in Rab44-knockout (KO) mice to investigate the effects of Rab44 on inflammation, cell filtration, and bone destruction. Results: Compared with wild-type (WT) mice, Rab44-KO mice showed reduced inflammation in arthritis under CAIA-inducing conditions. Rab44-KO CAIA mice exhibited reduced cell filtration in the radiocarpal joints. Consistent with these findings, Rab44-KO CAIA mice showed decreased mRNA levels of arthritis-related marker genes including genes for inflammation, cartilage turnover, bone formation, and bone absorption markers. Rab44-KO CAIA mice exhibited predominant infiltration of M2-type macrophages at inflammatory sites and reduced bone loss compared to WT CAIA mice. Conclusions: These results indicate that Rab44 deficiency reduces the progression of inflammation in CAIA in mice.
To continue reading and to download the publication:
