Featured Publication in Focus: Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Stimulates Proopiomelanocortin Transcription via the CaMKK/CaMKIV Pathway in the AtT20 Cell Line
Jul 30 , 2025
Authors:
Wenyi Jiang, Haotian Zhang, Hitomi Imachi, Toshihiro Kobayashi, Kensaku Fukunaga, Takanobu Saheki, Takafumi Yoshimura, Tao Dong, Guoxing Zhang and Koji Murao
Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Faculty of Medicine, Kagawa University, Kagawa, JPN
Cureus Journal of Medical Science. Springer Nature
----------------------
Product referenced:
Catalogue # M046006
----------------------
ABSTRACT
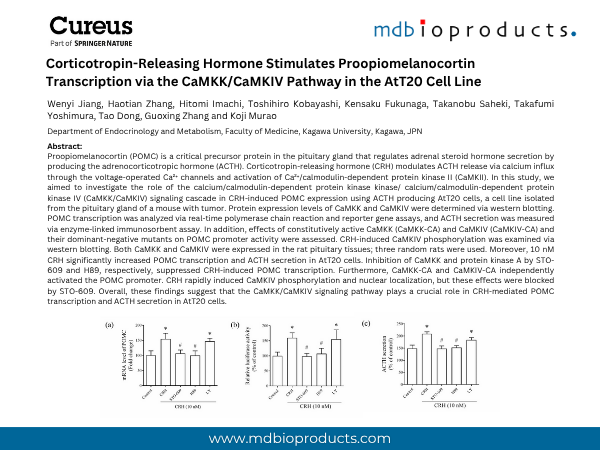
Proopiomelanocortin (POMC) is a critical precursor protein in the pituitary gland that regulates adrenal steroid hormone secretion by producing the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) modulates ACTH release via calcium influx through the voltage-operated Ca²⁺ channels and activation of Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). In this study, we aimed to investigate the role of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase/ calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV (CaMKK/CaMKIV) signaling cascade in CRH-induced POMC expression using ACTH-producing AtT20 cells, a cell line isolated from the pituitary gland of a mouse with tumor. Protein expression levels of CaMKK and CaMKIV were determined via western blotting. POMC transcription was analyzed via real-time polymerase chain reaction and reporter gene assays, and ACTH secretion was measured via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In addition, effects of constitutively active CaMKK (CaMKK-CA) and CaMKIV (CaMKIV-CA) and their dominant-negative mutants on POMC promoter activity were assessed. CRH-induced CaMKIV phosphorylation was examined via western blotting. Both CaMKK and CaMKIV were expressed in the rat pituitary tissues; three random rats were used. Moreover, 10 nM CRH significantly increased POMC transcription and ACTH secretion in AtT20 cells. Inhibition of CaMKK and protein kinase A by STO-609 and H89, respectively, suppressed CRH-induced POMC transcription. Furthermore, CaMKK-CA and CaMKIV-CA independently activated the POMC promoter. CRH rapidly induced CaMKIV phosphorylation and nuclear localization, but these effects were blocked by STO-609. Overall, these findings suggest that the CaMKK/CaMKIV signaling pathway plays a crucial role in CRH-mediated POMC transcription and ACTH secretion in AtT20 cells.
To continue reading and to download the publication:
