Featured Publication in Focus: Kidney Tubular Biomarkers in Type 1 Diabetes - Longitudinal Analysis of Two Cohorts
Aug 07 , 2025
Authors:
Christine P. Limonte, David K. Prince, Andrew N. Hoofnagle, Irl B. Hirsch, Sushrut S. Waikar, Alessandro Doria, Michael Mauer, Bryan R. Kestenbaum and Ian H. de Boer
Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Kidney International Reports. International Society of Nephrology
----------------------
Product referenced:
Catalogue # M036020
Uromodulin Glycoprotein (UMOD, Tamm-Horsfall Glycoprotein, THP) ELISA
----------------------
ABSTRACT
Background Kidney tubular biomarker trends may provide insight into tubulointerstitial pathology that is not evident through measurement of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and albumin excretion rate (AER).
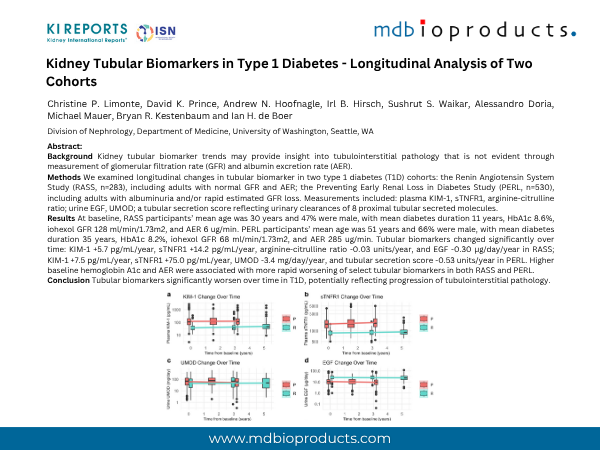
Methods We examined longitudinal changes in tubular biomarker in two type 1 diabetes (T1D) cohorts: the Renin Angiotensin System Study (RASS, n=283), including adults with normal GFR and AER; the Preventing Early Renal Loss in Diabetes Study (PERL, n=530), including adults with albuminuria and/or rapid estimated GFR loss. Measurements included: plasma KIM-1, sTNFR1, arginine-citrulline ratio; urine EGF, UMOD; a tubular secretion score reflecting urinary clearances of 8 proximal tubular secreted molecules.
Results At baseline, RASS participants’ mean age was 30 years and 47% were male, with mean diabetes duration 11 years, HbA1c 8.6%, iohexol GFR 128 ml/min/1.73m2, and AER 6 ug/min. PERL participants’ mean age was 51 years and 66% were male, with mean diabetes duration 35 years, HbA1c 8.2%, iohexol GFR 68 ml/min/1.73m2, and AER 285 ug/min. Tubular biomarkers changed significantly over time: KIM-1 +5.7 pg/mL/year, sTNFR1 +14.2 pg/mL/year, arginine-citrulline ratio -0.03 units/year, and EGF -0.30 µg/day/year in RASS; KIM-1 +7.5 pg/mL/year, sTNFR1 +75.0 pg/mL/year, UMOD -3.4 mg/day/year, and tubular secretion score -0.53 units/year in PERL. Higher baseline hemoglobin A1c and AER were associated with more rapid worsening of select tubular biomarkers in both RASS and PERL.
Conclusion Tubular biomarkers significantly worsen over time in T1D, potentially reflecting progression of tubulointerstitial pathology
To continue reading and to download the publication:
